Difference between revisions of "Standard Deviation"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 323: | Line 323: | ||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uk98hiMQgN0 Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean], The Organic Chemistry Tutor | * [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uk98hiMQgN0 Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean], The Organic Chemistry Tutor | ||
| − | == | + | == Licensing == |
| − | + | Content obtained and/or adapted from: | |
| − | + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_deviation Standard deviation, Wikipedia] under a CC BY-SA license | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 10:42, 30 October 2021
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range.
Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter sigma σ, for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter s, for the sample standard deviation.
The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice, less robust than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data.
The standard deviation of a population or sample and the standard error of a statistic (e.g., of the sample mean) are quite different, but related. The sample mean's standard error is the standard deviation of the set of means that would be found by drawing an infinite number of repeated samples from the population and computing a mean for each sample. The mean's standard error turns out to equal the population standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size, and is estimated by using the sample standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. For example, a poll's standard error (what is reported as the margin of error of the poll), is the expected standard deviation of the estimated mean if the same poll were to be conducted multiple times. Thus, the standard error estimates the standard deviation of an estimate, which itself measures how much the estimate depends on the particular sample that was taken from the population.
In science, it is common to report both the standard deviation of the data (as a summary statistic) and the standard error of the estimate (as a measure of potential error in the findings). By convention, only effects more than two standard errors away from a null expectation are considered "statistically significant", a safeguard against spurious conclusion that is really due to random sampling error.
When only a sample of data from a population is available, the term standard deviation of the sample or sample standard deviation can refer to either the above-mentioned quantity as applied to those data, or to a modified quantity that is an unbiased estimate of the population standard deviation (the standard deviation of the entire population).
Contents
Basic examples
Population standard deviation of grades of eight students
Suppose that the entire population of interest is eight students in a particular class. For a finite set of numbers, the population standard deviation is found by taking the square root of the average of the squared deviations of the values subtracted from their average value. The marks of a class of eight students (that is, a statistical population) are the following eight values:
These eight data points have the mean (average) of 5:
First, calculate the deviations of each data point from the mean, and square the result of each:
The variance is the mean of these values:
and the population standard deviation is equal to the square root of the variance:
This formula is valid only if the eight values with which we began form the complete population. If the values instead were a random sample drawn from some large parent population (for example, they were 8 students randomly and independently chosen from a class of 2 million), then one divides by 7 (which is n − 1) instead of 8 (which is n) in the denominator of the last formula, and the result is In that case, the result of the original formula would be called the sample standard deviation and denoted by s instead of Dividing by n − 1 rather than by n gives an unbiased estimate of the variance of the larger parent population. This is known as Bessel's correction. Roughly, the reason for it is that the formula for the sample variance relies on computing differences of observations from the sample mean, and the sample mean itself was constructed to be as close as possible to the observations, so just dividing by n would underestimate the variability.
Standard deviation of average height for adult men
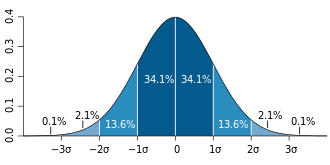
If the population of interest is approximately normally distributed, the standard deviation provides information on the proportion of observations above or below certain values. For example, the average height for adult men in the United States is about 70 inches (177.8 cm), with a standard deviation of around 3 inches (7.62 cm). This means that most men (about 68%, assuming a normal distribution) have a height within 3 inches (7.62 cm) of the mean (67–73 inches (170.18–185.42 cm)) - one standard deviation - and almost all men (about 95%) have a height within 6 inches (15.24 cm) of the mean (64–76 inches (162.56–193.04 cm)) - two standard deviations. If the standard deviation were zero, then all men would be exactly 70 inches (177.8 cm) tall. If the standard deviation were 20 inches (50.8 cm), then men would have much more variable heights, with a typical range of about 50–90 inches (127–228.6 cm). Three standard deviations account for 99.7% of the sample population being studied, assuming the distribution is normal or bell-shaped (see the 68-95-99.7 rule, or the empirical rule, for more information).
Definition of population values
Let μ be the expected value (the average) of random variable X with density f(x):
The standard deviation σ of X is defined as
which can be shown to equal
Using words, the standard deviation is the square root of the variance of X.
The standard deviation of a probability distribution is the same as that of a random variable having that distribution.
Not all random variables have a standard deviation. If the distribution has fat tails going out to infinity, the standard deviation might not exist, because the integral might not converge. The normal distribution has tails going out to infinity, but its mean and standard deviation do exist, because the tails diminish quickly enough. The Pareto distribution with parameter has a mean, but not a standard deviation (loosely speaking, the standard deviation is infinite). The Cauchy distribution has neither a mean nor a standard deviation.
Discrete random variable
In the case where X takes random values from a finite data set x1, x2, …, xN, with each value having the same probability, the standard deviation is
or, by using summation notation,
If, instead of having equal probabilities, the values have different probabilities, let x1 have probability p1, x2 have probability p2, …, xN have probability pN. In this case, the standard deviation will be
Continuous random variable
The standard deviation of a continuous real-valued random variable X with probability density function p(x) is
and where the integrals are definite integrals taken for x ranging over the set of possible values of the random variable X.
In the case of a parametric family of distributions, the standard deviation can be expressed in terms of the parameters. For example, in the case of the log-normal distribution with parameters μ and σ2, the standard deviation is
Estimation
One can find the standard deviation of an entire population in cases (such as standardized testing) where every member of a population is sampled. In cases where that cannot be done, the standard deviation σ is estimated by examining a random sample taken from the population and computing a statistic of the sample, which is used as an estimate of the population standard deviation. Such a statistic is called an estimator, and the estimator (or the value of the estimator, namely the estimate) is called a sample standard deviation, and is denoted by s (possibly with modifiers).
Unlike in the case of estimating the population mean, for which the sample mean is a simple estimator with many desirable properties (unbiased, efficient, maximum likelihood), there is no single estimator for the standard deviation with all these properties, and unbiased estimation of standard deviation is a very technically involved problem. Most often, the standard deviation is estimated using the corrected sample standard deviation (using N − 1), defined below, and this is often referred to as the "sample standard deviation", without qualifiers. However, other estimators are better in other respects: the uncorrected estimator (using N) yields lower mean squared error, while using N − 1.5 (for the normal distribution) almost completely eliminates bias.
Uncorrected sample standard deviation
The formula for the population standard deviation (of a finite population) can be applied to the sample, using the size of the sample as the size of the population (though the actual population size from which the sample is drawn may be much larger). This estimator, denoted by sN, is known as the uncorrected sample standard deviation, or sometimes the standard deviation of the sample (considered as the entire population), and is defined as follows:
where are the observed values of the sample items, and is the mean value of these observations, while the denominator N stands for the size of the sample: this is the square root of the sample variance, which is the average of the squared deviations about the sample mean.
This is a consistent estimator (it converges in probability to the population value as the number of samples goes to infinity), and is the maximum-likelihood estimate when the population is normally distributed. However, this is a biased estimator, as the estimates are generally too low. The bias decreases as sample size grows, dropping off as 1/N, and thus is most significant for small or moderate sample sizes; for the bias is below 1%. Thus for very large sample sizes, the uncorrected sample standard deviation is generally acceptable. This estimator also has a uniformly smaller mean squared error than the corrected sample standard deviation.
Corrected sample standard deviation
If the biased sample variance (the second central moment of the sample, which is a downward-biased estimate of the population variance) is used to compute an estimate of the population's standard deviation, the result is
Here taking the square root introduces further downward bias, by Jensen's inequality, due to the square root's being a concave function. The bias in the variance is easily corrected, but the bias from the square root is more difficult to correct, and depends on the distribution in question.
An unbiased estimator for the variance is given by applying Bessel's correction, using N − 1 instead of N to yield the unbiased sample variance, denoted s2:
This estimator is unbiased if the variance exists and the sample values are drawn independently with replacement. N − 1 corresponds to the number of degrees of freedom in the vector of deviations from the mean,
Taking square roots reintroduces bias (because the square root is a nonlinear function, which does not commute with the expectation), yielding the corrected sample standard deviation, denoted by s:
As explained above, while s2 is an unbiased estimator for the population variance, s is still a biased estimator for the population standard deviation, though markedly less biased than the uncorrected sample standard deviation. This estimator is commonly used and generally known simply as the "sample standard deviation". The bias may still be large for small samples (N less than 10). As sample size increases, the amount of bias decreases. We obtain more information and the difference between and becomes smaller.
Unbiased sample standard deviation
For unbiased estimation of standard deviation, there is no formula that works across all distributions, unlike for mean and variance. Instead, s is used as a basis, and is scaled by a correction factor to produce an unbiased estimate. For the normal distribution, an unbiased estimator is given by s/c4, where the correction factor (which depends on N) is given in terms of the Gamma function, and equals:
This arises because the sampling distribution of the sample standard deviation follows a (scaled) chi distribution, and the correction factor is the mean of the chi distribution.
An approximation can be given by replacing N − 1 with N − 1.5, yielding:
The error in this approximation decays quadratically (as 1/N2), and it is suited for all but the smallest samples or highest precision: for N = 3 the bias is equal to 1.3%, and for N = 9 the bias is already less than 0.1%.
A more accurate approximation is to replace above with .
For other distributions, the correct formula depends on the distribution, but a rule of thumb is to use the further refinement of the approximation:
where γ2 denotes the population excess kurtosis. The excess kurtosis may be either known beforehand for certain distributions, or estimated from the data.
Confidence interval of a sampled standard deviation
The standard deviation we obtain by sampling a distribution is itself not absolutely accurate, both for mathematical reasons (explained here by the confidence interval) and for practical reasons of measurement (measurement error). The mathematical effect can be described by the confidence interval or CI.
To show how a larger sample will make the confidence interval narrower, consider the following examples: A small population of N = 2 has only 1 degree of freedom for estimating the standard deviation. The result is that a 95% CI of the SD runs from 0.45 × SD to 31.9 × SD; the factors here are as follows:
where is the p-th quantile of the chi-square distribution with k degrees of freedom, and is the confidence level. This is equivalent to the following:
With k = 1, and . The reciprocals of the square roots of these two numbers give us the factors 0.45 and 31.9 given above.
A larger population of N = 10 has 9 degrees of freedom for estimating the standard deviation. The same computations as above give us in this case a 95% CI running from 0.69 × SD to 1.83 × SD. So even with a sample population of 10, the actual SD can still be almost a factor 2 higher than the sampled SD. For a sample population N=100, this is down to 0.88 × SD to 1.16 × SD. To be more certain that the sampled SD is close to the actual SD we need to sample a large number of points.
These same formulae can be used to obtain confidence intervals on the variance of residuals from a least squares fit under standard normal theory, where k is now the number of degrees of freedom for error.
Bounds on standard deviation
For a set of N > 4 data spanning a range of values R, an upper bound on the standard deviation s is given by s = 0.6R.
An estimate of the standard deviation for N > 100 data taken to be approximately normal follows from the heuristic that 95% of the area under the normal curve lies roughly two standard deviations to either side of the mean, so that, with 95% probability the total range of values R represents four standard deviations so that s ≈ R/4. This so-called range rule is useful in sample size estimation, as the range of possible values is easier to estimate than the standard deviation. Other divisors K(N) of the range such that s ≈ R/K(N) are available for other values of N and for non-normal distributions.
Identities and mathematical properties
The standard deviation is invariant under changes in location, and scales directly with the scale of the random variable. Thus, for a constant c and random variables X and Y:
The standard deviation of the sum of two random variables can be related to their individual standard deviations and the covariance between them:
where and stand for variance and covariance, respectively.
The calculation of the sum of squared deviations can be related to moments calculated directly from the data. In the following formula, the letter E is interpreted to mean expected value, i.e., mean.
The sample standard deviation can be computed as:
For a finite population with equal probabilities at all points, we have
which means that the standard deviation is equal to the square root of the difference between the average of the squares of the values and the square of the average value.
See computational formula for the variance for proof, and for an analogous result for the sample standard deviation.
Interpretation and application
A large standard deviation indicates that the data points can spread far from the mean and a small standard deviation indicates that they are clustered closely around the mean.
For example, each of the three populations {0, 0, 14, 14}, {0, 6, 8, 14} and {6, 6, 8, 8} has a mean of 7. Their standard deviations are 7, 5, and 1, respectively. The third population has a much smaller standard deviation than the other two because its values are all close to 7. These standard deviations have the same units as the data points themselves. If, for instance, the data set {0, 6, 8, 14} represents the ages of a population of four siblings in years, the standard deviation is 5 years. As another example, the population {1000, 1006, 1008, 1014} may represent the distances traveled by four athletes, measured in meters. It has a mean of 1007 meters, and a standard deviation of 5 meters.
Standard deviation may serve as a measure of uncertainty. In physical science, for example, the reported standard deviation of a group of repeated measurements gives the precision of those measurements. When deciding whether measurements agree with a theoretical prediction, the standard deviation of those measurements is of crucial importance: if the mean of the measurements is too far away from the prediction (with the distance measured in standard deviations), then the theory being tested probably needs to be revised. This makes sense since they fall outside the range of values that could reasonably be expected to occur, if the prediction were correct and the standard deviation appropriately quantified.
While the standard deviation does measure how far typical values tend to be from the mean, other measures are available. An example is the mean absolute deviation, which might be considered a more direct measure of average distance, compared to the root mean square distance inherent in the standard deviation.
Relationship between standard deviation and mean
The mean and the standard deviation of a set of data are descriptive statistics usually reported together. In a certain sense, the standard deviation is a "natural" measure of statistical dispersion if the center of the data is measured about the mean. This is because the standard deviation from the mean is smaller than from any other point. The precise statement is the following: suppose x1, ..., xn are real numbers and define the function:
Using calculus or by completing the square, it is possible to show that σ(r) has a unique minimum at the mean:
Variability can also be measured by the coefficient of variation, which is the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean. It is a dimensionless number.
Standard deviation of the mean
Often, we want some information about the precision of the mean we obtained. We can obtain this by determining the standard deviation of the sampled mean. Assuming statistical independence of the values in the sample, the standard deviation of the mean is related to the standard deviation of the distribution by:
where N is the number of observations in the sample used to estimate the mean. This can easily be proven with (see basic properties of the variance):
(Statistical independence is assumed.)
hence
Resulting in:
In order to estimate the standard deviation of the mean it is necessary to know the standard deviation of the entire population beforehand. However, in most applications this parameter is unknown. For example, if a series of 10 measurements of a previously unknown quantity is performed in a laboratory, it is possible to calculate the resulting sample mean and sample standard deviation, but it is impossible to calculate the standard deviation of the mean.
Rapid calculation methods
The following two formulas can represent a running (repeatedly updated) standard deviation. A set of two power sums s1 and s2 are computed over a set of N values of x, denoted as x1, ..., xN:
Given the results of these running summations, the values N, s1, s2 can be used at any time to compute the current value of the running standard deviation:
Where N, as mentioned above, is the size of the set of values (or can also be regarded as s0).
Similarly for sample standard deviation,
In a computer implementation, as the two sj sums become large, we need to consider round-off error, arithmetic overflow, and arithmetic underflow. The method below calculates the running sums method with reduced rounding errors. This is a "one pass" algorithm for calculating variance of n samples without the need to store prior data during the calculation. Applying this method to a time series will result in successive values of standard deviation corresponding to n data points as n grows larger with each new sample, rather than a constant-width sliding window calculation.
For k = 1, ..., n:
where A is the mean value.
Note: since or
Sample variance:
Population variance:
Weighted calculation
When the values xi are weighted with unequal weights wi, the power sums s0, s1, s2 are each computed as:
And the standard deviation equations remain unchanged. s0 is now the sum of the weights and not the number of samples N.
The incremental method with reduced rounding errors can also be applied, with some additional complexity.
A running sum of weights must be computed for each k from 1 to n:
and places where 1/n is used above must be replaced by wi/Wn:
In the final division,
and
or
where n is the total number of elements, and n' is the number of elements with non-zero weights.
The above formulas become equal to the simpler formulas given above if weights are taken as equal to one.
Resources
- How To Calculate The Standard Deviation, The Organic Chemistry Tutor
- Standard Deviation Formula, Statistics, Variance, Sample and Population Mean, The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Licensing
Content obtained and/or adapted from:
- Standard deviation, Wikipedia under a CC BY-SA license








![{\displaystyle \mu \equiv \operatorname {E} [X]=\int _{-\infty }^{+\infty }xf(x)dx\!}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a52450bdb5f362a80d7612f714e99f674188d846)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\sigma &\equiv {\sqrt {\operatorname {E} \left[(X-\mu )^{2}\right]}}={\sqrt {\int _{-\infty }^{+\infty }(x-\mu )^{2}f(x)dx}},\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/50fc45dec3e6e45e6b06bb50ea4d218269049d94)
![{\textstyle {\sqrt {\operatorname {E} \left[X^{2}\right]-(\operatorname {E} [X])^{2}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e2dd8d466c3ecb05713377fefcb7e7f787b29ce7)
![{\displaystyle \alpha \in (1,2]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/782b1d598278b0238ee817c658744e8a7ed3a06e)
![{\displaystyle \sigma ={\sqrt {{\frac {1}{N}}\left[(x_{1}-\mu )^{2}+(x_{2}-\mu )^{2}+\cdots +(x_{N}-\mu )^{2}\right]}},{\text{ where }}\mu ={\frac {1}{N}}(x_{1}+\cdots +x_{N}),}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/827beb1be760eed3cb07b20d29f01d326f728071)





























![{\displaystyle \sigma (X)={\sqrt {\operatorname {E} \left[(X-\operatorname {E} [X])^{2}\right]}}={\sqrt {\operatorname {E} \left[X^{2}\right]-(\operatorname {E} [X])^{2}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d3ab12089bd2027790ef060ff7cc2ec05ae2021f)
![{\displaystyle s(X)={\sqrt {\frac {N}{N-1}}}{\sqrt {\operatorname {E} \left[(X-\operatorname {E} [X])^{2}\right]}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/702e9da21c721697e6e81932bf8b7443028f7d6d)


























