Difference between revisions of "Linear Functions and Slope"
(Created page with "thumb|right|Graph of the linear function: <math>y(x) = -x + 2</math> In calculus and related areas of mathematics, a '''linear function''' f...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
==Relationship with linear equations== | ==Relationship with linear equations== | ||
[[Image:wiki linearna funkcija eks1.png|thumb|right]]<!-- are PNG and a translit from a foreign language necessary? --> | [[Image:wiki linearna funkcija eks1.png|thumb|right]]<!-- are PNG and a translit from a foreign language necessary? --> | ||
| − | Linear functions commonly arise from practical problems involving variables <math>x,y</math> with a linear relationship, that is, obeying a | + | Linear functions commonly arise from practical problems involving variables <math>x,y</math> with a linear relationship, that is, obeying a linear equation <math>Ax+By=C</math>. If <math>B\neq 0</math>, one can solve this equation for ''y'', obtaining |
:<math>y = -\tfrac{A}{B}x +\tfrac{C}{B}=ax+b,</math> | :<math>y = -\tfrac{A}{B}x +\tfrac{C}{B}=ax+b,</math> | ||
where we denote <math>a=-\tfrac{A}{B}</math> and <math>b=\tfrac{C}{B}</math>. That is, one may consider ''y'' as a dependent variable (output) obtained from the independent variable (input) ''x'' via a linear function: <math>y = f(x) = ax+b</math>. In the ''xy''-coordinate plane, the possible values of <math>(x,y)</math> form a line, the graph of the function <math>f(x)</math>. If <math>B=0</math> in the original equation, the resulting line <math>x=\tfrac{C}{A}</math> is vertical, and cannot be written as <math>y=f(x)</math>. | where we denote <math>a=-\tfrac{A}{B}</math> and <math>b=\tfrac{C}{B}</math>. That is, one may consider ''y'' as a dependent variable (output) obtained from the independent variable (input) ''x'' via a linear function: <math>y = f(x) = ax+b</math>. In the ''xy''-coordinate plane, the possible values of <math>(x,y)</math> form a line, the graph of the function <math>f(x)</math>. If <math>B=0</math> in the original equation, the resulting line <math>x=\tfrac{C}{A}</math> is vertical, and cannot be written as <math>y=f(x)</math>. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
* [https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-algebra/chapter/introduction-to-linear-functions/ Introduction to Linear Functions], Lumen Learning | * [https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-algebra/chapter/introduction-to-linear-functions/ Introduction to Linear Functions], Lumen Learning | ||
| − | == | + | == Licensing == |
| − | * | + | Content obtained and/or adapted from: |
| − | + | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linear_function_(calculus) Linear function (Calculus), Wikipedia] under a CC BY-SA license | |
Latest revision as of 22:52, 13 November 2021
In calculus and related areas of mathematics, a linear function from the real numbers to the real numbers is a function whose graph (in Cartesian coordinates) is a line in the plane. The characteristic property of linear functions is that when the input variable is changed, the change in the output is proportional to the change in the input.
Linear functions are related to linear equations.
Contents
Properties
A linear function is a polynomial function in which the variable x has degree at most one:
- .
Such a function is called linear because its graph, the set of all points in the Cartesian plane, is a line. The coefficient a is called the slope of the function and of the line (see below).
If the slope is , this is a constant function defining a horizontal line, which some authors exclude from the class of linear functions. With this definition, the degree of a linear polynomial would be exactly one, and its graph would be a line that is neither vertical nor horizontal. However, in this article, is required, so constant functions will be considered linear.
If then the linear function is said to be homogeneous. Such function defines a line that passes through the origin of the coordinate system, that is, the point . In advanced mathematics texts, the term linear function often denotes specifically homogeneous linear functions, while the term affine function is used for the general case, which includes Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b\neq0} .
The natural domain of a linear function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} , the set of allowed input values for x, is the entire set of real numbers, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\in \mathbb R.} One can also consider such functions with x in an arbitrary field, taking the coefficients a, b in that field.
The graph Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)=ax+b} is a non-vertical line having exactly one intersection with the y-axis, its y-intercept point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x,y)=(0,b).} The y-intercept value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(0)=b} is also called the initial value of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x).} If Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a\neq 0,} the graph is a non-horizontal line having exactly one intersection with the x-axis, the x-intercept point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x,y)=(-\tfrac ba,0).} The x-intercept value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=-\tfrac ba,} the solution of the equation Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)=0,} is also called the root or zero of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x).}
Slope
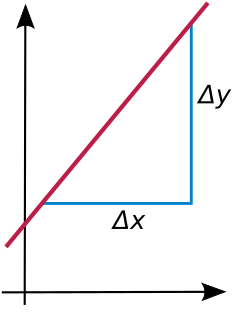
The slope of a nonvertical line is a number that measures how steeply the line is slanted (rise-over-run). If the line is the graph of the linear function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = ax + b} , this slope is given by the constant a.
The slope measures the constant rate of change of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} per unit change in x: whenever the input x is increased by one unit, the output changes by a units: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x{+}1)=f(x)+a} , and more generally Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x{+}\Delta x)=f(x)+a\Delta x} for any number Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta x} . If the slope is positive, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a > 0} , then the function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} is increasing; if Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a < 0} , then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} is decreasing
In calculus, the derivative of a general function measures its rate of change. A linear function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)=ax+b} has a constant rate of change equal to its slope a, so its derivative is the constant function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f\,'(x)=a} .
The fundamental idea of differential calculus is that any smooth function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} (not necessarily linear) can be closely approximated near a given point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=c} by a unique linear function. The derivative Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f\,'(c)} is the slope of this linear function, and the approximation is: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) \approx f\,'(c)(x{-}c)+f(c)} for Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\approx c} . The graph of the linear approximation is the tangent line of the graph Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)} at the point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (c,f(c))} . The derivative slope Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f\,'(c)} generally varies with the point c. Linear functions can be characterized as the only real functions whose derivative is constant: if Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f\,'(x)=a} for all x, then Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)=ax+b} for Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b=f(0)} .
Slope-intercept, point-slope, and two-point forms
A given linear function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} can be written in several standard formulas displaying its various properties. The simplest is the slope-intercept form:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)= ax+b} ,
from which one can immediately see the slope a and the initial value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(0)=b} , which is the y-intercept of the graph Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)} .
Given a slope a and one known value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_0)=y_0} , we write the point-slope form:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = a(x{-}x_0)+y_0} .
In graphical terms, this gives the line with slope a passing through the point .
The two-point form starts with two known values Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_0)=y_0} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_1)=y_1} . One computes the slope Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a=\tfrac{y_1-y_0}{x_1-x_0}} and inserts this into the point-slope form:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = \tfrac{y_1-y_0}{x_1-x_0}(x{-}x_0\!) + y_0} .
Its graph Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)} is the unique line passing through the points Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x_0,y_0\!), (x_1,y_1\!)} . The equation Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)} may also be written to emphasize the constant slope:
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{y-y_0}{x-x_0}=\frac{y_1-y_0}{x_1-x_0}} .
Relationship with linear equations
Linear functions commonly arise from practical problems involving variables Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x,y} with a linear relationship, that is, obeying a linear equation Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Ax+By=C} . If Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B\neq 0} , one can solve this equation for y, obtaining
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = -\tfrac{A}{B}x +\tfrac{C}{B}=ax+b,}
where we denote Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a=-\tfrac{A}{B}} and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b=\tfrac{C}{B}} . That is, one may consider y as a dependent variable (output) obtained from the independent variable (input) x via a linear function: Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = f(x) = ax+b} . In the xy-coordinate plane, the possible values of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x,y)} form a line, the graph of the function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} . If Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=0} in the original equation, the resulting line Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=\tfrac{C}{A}} is vertical, and cannot be written as Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(x)} .
The features of the graph Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = f(x) = ax+b} can be interpreted in terms of the variables x and y. The y-intercept is the initial value Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=f(0)=b} at Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0} . The slope a measures the rate of change of the output y per unit change in the input x. In the graph, moving one unit to the right (increasing x by 1) moves the y-value up by a: that is, Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x{+}1) = f(x) + a} . Negative slope a indicates a decrease in y for each increase in x.
For example, the linear function Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = -2x + 4} has slope Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a=-2} , y-intercept point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (0,b)=(0,4)} , and x-intercept point Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (2,0)} .
Resources
- Introduction to Linear Functions, Lumen Learning
Licensing
Content obtained and/or adapted from:
- Linear function (Calculus), Wikipedia under a CC BY-SA license










