Difference between revisions of "Absolute Value Functions"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
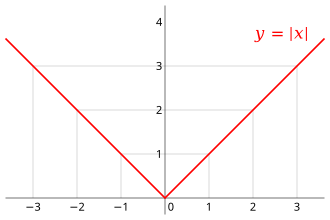
[[Image:Absolute value.svg|thumb|The [[graph of a function|graph]] of the absolute value function for real numbers]] | [[Image:Absolute value.svg|thumb|The [[graph of a function|graph]] of the absolute value function for real numbers]] | ||
| + | In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, denoted |x|, is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. Namely, |x| = x if x is positive, and |x| = −x if x is negative (in which case −x is positive), and |0| = 0. For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its "distance from zero". The absolute value function f(x) = |a| can be expressed as a piecewise function, where f(x) = a when a ≥ 0, and f(x) = -a when a < 0. We can use this to help us visualize and graph other absolute value functions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here are some examples of absolute value functions: | ||
| + | * <math> g(x) = |5x + 5| </math>. 5x + 5 ≥ 0 when x ≥ -1, and 5x + 5 < 0 when x < -1. So, g(x) = 5x + 5 when x ≥ -1, and g(x) = -5x - 5 when x < -1. | ||
| + | * h(x) = || | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Resources== | ||
Revision as of 11:51, 15 September 2021
Introduction

The graph of the absolute value function for real numbers
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, denoted |x|, is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. Namely, |x| = x if x is positive, and |x| = −x if x is negative (in which case −x is positive), and |0| = 0. For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its "distance from zero". The absolute value function f(x) = |a| can be expressed as a piecewise function, where f(x) = a when a ≥ 0, and f(x) = -a when a < 0. We can use this to help us visualize and graph other absolute value functions.
Here are some examples of absolute value functions:
- . 5x + 5 ≥ 0 when x ≥ -1, and 5x + 5 < 0 when x < -1. So, g(x) = 5x + 5 when x ≥ -1, and g(x) = -5x - 5 when x < -1.
- h(x) = ||
