Difference between revisions of "The Cross Product"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Cross product parallelogram.svg|Cross_product_parallelogram]] | + | [[File:Cross product parallelogram.svg|thumb|Cross_product_parallelogram]] |
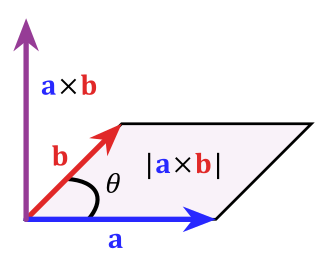
The cross product is an operation between two 3-dimensional vectors that returns a third vector orthogonal (i.e., perpendicular) to the first two. For vectors <math> \mathbf{u} = \langle u_1, u_2, u_3 \rangle </math> and <math> \mathbf{v} = \langle v_1, v_2, v_3 \rangle </math>, the cross product of <math> \mathbf{u} </math> and <math> \mathbf{v} </math> (notated as <math> u \times v </math>) is <math> \mathbf{w} = \langle u_2v_3 - u_3v_2, -(u_1v_3 - u_3v_1), u_1v_2 - u_2v_1 \rangle</math>. | The cross product is an operation between two 3-dimensional vectors that returns a third vector orthogonal (i.e., perpendicular) to the first two. For vectors <math> \mathbf{u} = \langle u_1, u_2, u_3 \rangle </math> and <math> \mathbf{v} = \langle v_1, v_2, v_3 \rangle </math>, the cross product of <math> \mathbf{u} </math> and <math> \mathbf{v} </math> (notated as <math> u \times v </math>) is <math> \mathbf{w} = \langle u_2v_3 - u_3v_2, -(u_1v_3 - u_3v_1), u_1v_2 - u_2v_1 \rangle</math>. | ||
| − | <math> \begin{vmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{vmatrix} </ | + | <math> \begin{vmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{vmatrix} </math> |
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
* [https://openstax.org/books/calculus-volume-3/pages/2-4-the-cross-product The Cross Product], OpenStax | * [https://openstax.org/books/calculus-volume-3/pages/2-4-the-cross-product The Cross Product], OpenStax | ||
* [https://omega0.xyz/omega8008/calc3/cross-product-dir/cornell-lecture.html Cross Product], Cornell University | * [https://omega0.xyz/omega8008/calc3/cross-product-dir/cornell-lecture.html Cross Product], Cornell University | ||
Revision as of 17:21, 20 September 2021
The cross product is an operation between two 3-dimensional vectors that returns a third vector orthogonal (i.e., perpendicular) to the first two. For vectors and , the cross product of and (notated as ) is .
Resources
- The Cross Product, OpenStax
- Cross Product, Cornell University