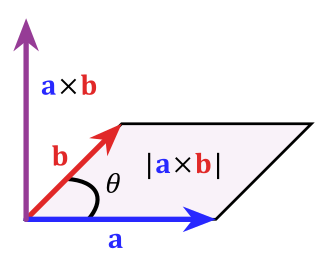
Cross_product_parallelogram
The cross product is an operation between two 3-dimensional vectors that returns a third vector orthogonal (i.e., perpendicular) to the first two. For vectors  and
and  , the cross product of
, the cross product of  and
and  (notated as
(notated as  ) is
) is  . The magnitude of the cross product,
. The magnitude of the cross product,  , equals the area of the parallelogram created by adding vector
, equals the area of the parallelogram created by adding vector  to vector
to vector  , and adding
, and adding  to
to  (see image).
(see image).
One way to remember the cross product of  and
and  is to calculate it with the following determinant:
is to calculate it with the following determinant:

Resources








