Convergent Sequences in Metric Spaces
Limits of Sequences in Metric Spaces
Recall that if a sequence of real numbers Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x_n)_{n=1}^{\infty} = (x_1, x_2, ..., x_n, ...)} is an infinite ordered list where for every . We will now generalize the concept of a sequence to contain elements from a metric space .
Definition: Let be a metric space. An (infinite) Sequence in denoted is an infinite ordered list of elements for all .
Finite sequences in a metric space can be defined as a finite ordered list of elements in but their study is not that interesting to us.
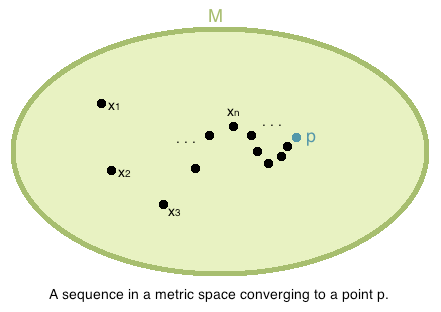
We can also define whether a sequence of elements from a metric space converges or diverges.
Definition: Let be a metric space. A sequence in is said to be Convergent to the element written if and the element is said to be the Limit of the sequence . If no such exists, then is said to be Divergent.
There is a subtle but important point to make. In the definition above, represents the limit of a sequence of elements from the metric space to an element while represents the limit of a sequence of positive real numbers to - such limits we already have experience with.
For example, if is any nonempty set, is the discrete metric, and , then the sequence defined by Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_n = x} for all Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \in \{ 1, 2, ... \}} , then the sequence:
Furthermore, it's not hard to see that this sequence converges to Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} , i.e., Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty} x_n = x} , i.e., Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty} d(x_n, x) = 0} since for all Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_n} we have that Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d(x_n, x) = 0} , so Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lim_{n \to \infty} d(x_n, x) = \lim_{n \to \infty} 0 = 0} .
We will soon see that many of theorems regarding limits of sequences of real numbers are analogous to limits of sequences of elements from metric spaces.