Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions

The sine and cosine functions have several distinct characteristics:
- They are periodic functions.
- The domain of each function is and the range is [−1,1].
- The graph of is symmetric about the origin.
- The graph of is symmetric about the y-axis.
- Given or Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = A\cos{(\omega x)} } for some real numbers Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A } and Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega} :
- The amplitude of the function is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |A| } , and represents the maximum distance from the x-axis that the function covers.
- The period (the distance between two peaks or two valleys) is Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{2\pi}{\omega} } , and represents one full "cycle" of the function.
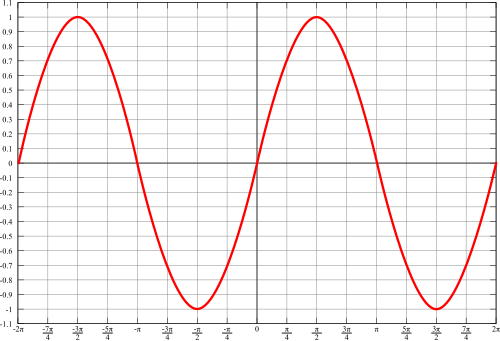
The graph of the sine function looks like this:
Careful analysis of this graph will show that the graph corresponds to the unit circle. x is essentially the degree measure (in radians), while y is the value of the sine function.
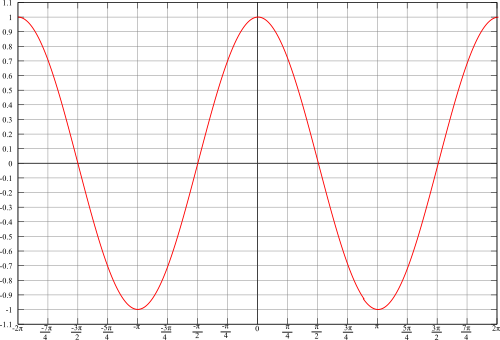
The graph of the cosine function looks like this:
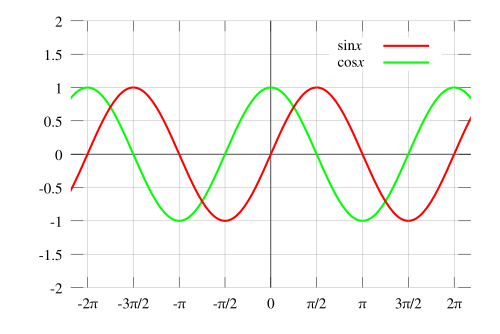
As with the sine function, analysis of the cosine function will show that the graph corresponds to the unit circle. One of the most important differences between the sine and cosine functions is that sine is an odd function (i.e. Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sin(-\theta)=-\sin(\theta)} while cosine is an even function (i.e. Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \cos(-\theta)=\cos(\theta)} .
Sine and cosine are periodic functions; that is, the above is repeated for preceding and following intervals with length Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2\pi} .
Resources
- Graphs of the Sine and Cosine. Written notes created by Professor Esparza, UTSA.
- Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions, Lumen Learning
Licensing
Content obtained and/or adapted from:
- Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions, Lumen Learning Precalculus II under a CC BY license
- Graphs of sine and cosine functions, Wikibooks: Trigonometry under a CC BY-SA license