Base 10, Base 2 & Base 5
In a positional numeral system, the radix or base is the number of unique digits, including the digit zero, used to represent numbers. For example, for the decimal/denary system (the most common system in use today) the radix (base number) is ten, because it uses the ten digits from 0 through 9.
In any standard positional numeral system, a number is conventionally written as (x)y with x as the string of digits and y as its base, although for base ten the subscript is usually assumed (and omitted, together with the pair of parentheses), as it is the most common way to express value. For example, (100)10 is equivalent to 100 (the decimal system is implied in the latter) and represents the number one hundred, while (100)2 (in the binary system with base 2) represents the number four.
Contents
In numeral systems
In the system with radix 13, for example, a string of digits such as 398 denotes the (decimal) number 3 × 132 + 9 × 131 + 8 × 130 = 632.
More generally, in a system with radix b (b > 1), a string of digits d1 … dn denotes the number d1bn−1 + d2bn−2 + … + dnb0, where 0 ≤ di < b. In contrast to decimal, or radix 10, which has a ones' place, tens' place, hundreds' place, and so on, radix b would have a ones' place, then a b1s' place, a b2s' place, etc.
Commonly used numeral systems include:
| Base/radix | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Binary numeral system | Used internally by nearly all computers, is base 2. The two digits are "0" and "1", expressed from switches displaying OFF and ON, respectively. Used in most electric counters. |
| 8 | Octal system | Used occasionally in computing. The eight digits are "0"–"7" and represent 3 bits (23). |
| 10 | Decimal system | Used by humans in the vast majority of cultures. Its ten digits are "0"–"9". Used in most mechanical counters. |
| 12 | Duodecimal (dozenal) system | Sometimes advocated due to divisibility by 2, 3, 4, and 6. It was traditionally used as part of quantities expressed in dozens and grosses. |
| 16 | Hexadecimal system | Often used in computing as a more compact representation of binary (1 hex digit per 4 bits). The sixteen digits are "0"–"9" followed by "A"–"F" or "a"–"f". |
| 20 | Vigesimal system | Traditional numeral system in several cultures, still used by some for counting. Historically also known as the score system in English, now most famous in the phrase "four score and seven years ago" in the Gettysburg Address. |
| 60 | Sexagesimal system | Originated in ancient Sumer and passed to the Babylonians. Used today as the basis of modern circular coordinate system (degrees, minutes, and seconds) and time measuring (minutes, and seconds) by analogy to the rotation of the Earth. |
Base 2
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method of mathematical expression which uses only two symbols: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one).
The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language.
Representation
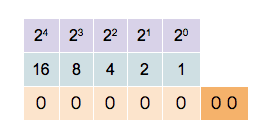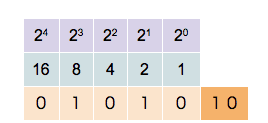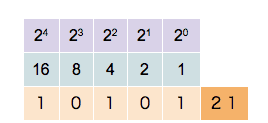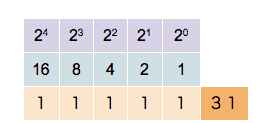
Any number can be represented by a sequence of bits (binary digits), which in turn may be represented by any mechanism capable of being in two mutually exclusive states. Any of the following rows of symbols can be interpreted as the binary numeric value of 667:
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| | | ― | | | ― | ― | | | | | ― | | | | |
| ☒ | ☐ | ☒ | ☐ | ☐ | ☒ | ☒ | ☐ | ☒ | ☒ |
| y | n | y | n | n | y | y | n | y | y |

The numeric value represented in each case is dependent upon the value assigned to each symbol. In the earlier days of computing, switches, punched holes and punched paper tapes were used to represent binary values.[1] In a modern computer, the numeric values may be represented by two different voltages; on a magnetic disk, magnetic polarities may be used. A "positive", "yes", or "on" state is not necessarily equivalent to the numerical value of one; it depends on the architecture in use.
In keeping with customary representation of numerals using Arabic numerals, binary numbers are commonly written using the symbols 0 and 1. When written, binary numerals are often subscripted, prefixed or suffixed in order to indicate their base, or radix. The following notations are equivalent:
- 100101 binary (explicit statement of format)
- 100101b (a suffix indicating binary format; also known as Intel convention[2][3])
- 100101B (a suffix indicating binary format)
- bin 100101 (a prefix indicating binary format)
- 1001012 (a subscript indicating base-2 (binary) notation)
- %100101 (a prefix indicating binary format; also known as Motorola convention[2][3])
- 0b100101 (a prefix indicating binary format, common in programming languages)
- 6b100101 (a prefix indicating number of bits in binary format, common in programming languages)
- #b100101 (a prefix indicating binary format, common in Lisp programming languages)
When spoken, binary numerals are usually read digit-by-digit, in order to distinguish them from decimal numerals. For example, the binary numeral 100 is pronounced one zero zero, rather than one hundred, to make its binary nature explicit, and for purposes of correctness. Since the binary numeral 100 represents the value four, it would be confusing to refer to the numeral as one hundred (a word that represents a completely different value, or amount). Alternatively, the binary numeral 100 can be read out as "four" (the correct value), but this does not make its binary nature explicit.
Counting in binary
Template:Aligned table Counting in binary is similar to counting in any other number system. Beginning with a single digit, counting proceeds through each symbol, in increasing order. Before examining binary counting, it is useful to briefly discuss the more familiar decimal counting system as a frame of reference.
Decimal counting
Decimal counting uses the ten symbols 0 through 9. Counting begins with the incremental substitution of the least significant digit (rightmost digit) which is often called the first digit. When the available symbols for this position are exhausted, the least significant digit is reset to 0, and the next digit of higher significance (one position to the left) is incremented (overflow), and incremental substitution of the low-order digit resumes. This method of reset and overflow is repeated for each digit of significance. Counting progresses as follows:
- 000, 001, 002, ... 007, 008, 009, (rightmost digit is reset to zero, and the digit to its left is incremented)
- 010, 011, 012, ...
- ...
- 090, 091, 092, ... 097, 098, 099, (rightmost two digits are reset to zeroes, and next digit is incremented)
- 100, 101, 102, ...
Binary counting
Binary counting follows the same procedure, except that only the two symbols 0 and 1 are available. Thus, after a digit reaches 1 in binary, an increment resets it to 0 but also causes an increment of the next digit to the left:
- 0000,
- 0001, (rightmost digit starts over, and next digit is incremented)
- 0010, 0011, (rightmost two digits start over, and next digit is incremented)
- 0100, 0101, 0110, 0111, (rightmost three digits start over, and the next digit is incremented)
- 1000, 1001, 1010, 1011, 1100, 1101, 1110, 1111 ...
In the binary system, each digit represents an increasing power of 2, with the rightmost digit representing 20, the next representing 21, then 22, and so on. The value of a binary number is the sum of the powers of 2 represented by each "1" digit. For example, the binary number 100101 is converted to decimal form as follows:
- 1001012 = [ ( 1 ) × 25 ] + [ ( 0 ) × 24 ] + [ ( 0 ) × 23 ] + [ ( 1 ) × 22 ] + [ ( 0 ) × 21 ] + [ ( 1 ) × 20 ]
- 1001012 = [ 1 × 32 ] + [ 0 × 16 ] + [ 0 × 8 ] + [ 1 × 4 ] + [ 0 × 2 ] + [ 1 × 1 ]
- 1001012 = 3710
Fractions
Fractions in binary arithmetic terminate only if 2 is the only prime factor in the denominator. As a result, 1/10 does not have a finite binary representation (10 has prime factors 2 and 5). This causes 10 × 0.1 not to precisely equal 1 in floating-point arithmetic. As an example, to interpret the binary expression for 1/3 = .010101..., this means: 1/3 = 0 × 2−1 + 1 × 2−2 + 0 × 2−3 + 1 × 2−4 + ... = 0.3125 + ... An exact value cannot be found with a sum of a finite number of inverse powers of two, the zeros and ones in the binary representation of 1/3 alternate forever.
| Fraction | Decimal | Binary | Fractional approximation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/1 | 1Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.999... | 1Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.111... | 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8... |
| 1/2 | 0.5Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.4999... | 0.1Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.0111... | 1/4 + 1/8 + 1/16 . . . |
| 1/3 | 0.333... | 0.010101... | 1/4 + 1/16 + 1/64 . . . |
| 1/4 | 0.25Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.24999... | 0.01Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.00111... | 1/8 + 1/16 + 1/32 . . . |
| 1/5 | 0.2Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.1999... | 0.00110011... | 1/8 + 1/16 + 1/128 . . . |
| 1/6 | 0.1666... | 0.0010101... | 1/8 + 1/32 + 1/128 . . . |
| 1/7 | 0.142857142857... | 0.001001... | 1/8 + 1/64 + 1/512 . . . |
| 1/8 | 0.125Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.124999... | 0.001Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.000111... | 1/16 + 1/32 + 1/64 . . . |
| 1/9 | 0.111... | 0.000111000111... | 1/16 + 1/32 + 1/64 . . . |
| 1/10 | 0.1Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.0999... | 0.000110011... | 1/16 + 1/32 + 1/256 . . . |
| 1/11 | 0.090909... | 0.00010111010001011101... | 1/16 + 1/64 + 1/128 . . . |
| 1/12 | 0.08333... | 0.00010101... | 1/16 + 1/64 + 1/256 . . . |
| 1/13 | 0.076923076923... | 0.000100111011000100111011... | 1/16 + 1/128 + 1/256 . . . |
| 1/14 | 0.0714285714285... | 0.0001001001... | 1/16 + 1/128 + 1/1024 . . . |
| 1/15 | 0.0666... | 0.00010001... | 1/16 + 1/256 . . . |
| 1/16 | 0.0625Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.0624999... | 0.0001Template:PadorTemplate:Pad0.0000111... | 1/32 + 1/64 + 1/128 . . . |
Binary arithmetic
Arithmetic in binary is much like arithmetic in other numeral systems. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can be performed on binary numerals.
Addition

The simplest arithmetic operation in binary is addition. Adding two single-digit binary numbers is relatively simple, using a form of carrying:
- 0 + 0 → 0
- 0 + 1 → 1
- 1 + 0 → 1
- 1 + 1 → 0, carry 1 (since 1 + 1 = 2 = 0 + (1 × 21) )
Adding two "1" digits produces a digit "0", while 1 will have to be added to the next column. This is similar to what happens in decimal when certain single-digit numbers are added together; if the result equals or exceeds the value of the radix (10), the digit to the left is incremented:
- 5 + 5 → 0, carry 1 (since 5 + 5 = 10 = 0 + (1 × 101) )
- 7 + 9 → 6, carry 1 (since 7 + 9 = 16 = 6 + (1 × 101) )
This is known as carrying. When the result of an addition exceeds the value of a digit, the procedure is to "carry" the excess amount divided by the radix (that is, 10/10) to the left, adding it to the next positional value. This is correct since the next position has a weight that is higher by a factor equal to the radix. Carrying works the same way in binary:
Template:Brown 0 1 1 0 1 + 1 0 1 1 1 ------------- = 1 0 0 1 0 0 = 36
In this example, two numerals are being added together: 011012 (1310) and 101112 (2310). The top row shows the carry bits used. Starting in the rightmost column, 1 + 1 = 102. The 1 is carried to the left, and the 0 is written at the bottom of the rightmost column. The second column from the right is added: 1 + 0 + 1 = 102 again; the 1 is carried, and 0 is written at the bottom. The third column: 1 + 1 + 1 = 112. This time, a 1 is carried, and a 1 is written in the bottom row. Proceeding like this gives the final answer 1001002 (3610).
When computers must add two numbers, the rule that: x xor y = (x + y) mod 2 for any two bits x and y allows for very fast calculation, as well.
Long carry method
A simplification for many binary addition problems is the Long Carry Method or Brookhouse Method of Binary Addition. This method is generally useful in any binary addition in which one of the numbers contains a long "string" of ones. It is based on the simple premise that under the binary system, when given a "string" of digits composed entirely of Template:Varserif ones (where Template:Varserif is any integer length), adding 1 will result in the number 1 followed by a string of Template:Var zeros. That concept follows, logically, just as in the decimal system, where adding 1 to a string of Template:Varserif 9s will result in the number 1 followed by a string of Template:Var 0s:
Binary Decimal
1 1 1 1 1 likewise 9 9 9 9 9
+ 1 + 1
——————————— ———————————
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Such long strings are quite common in the binary system. From that one finds that large binary numbers can be added using two simple steps, without excessive carry operations. In the following example, two numerals are being added together: 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 02 (95810) and 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 12 (69110), using the traditional carry method on the left, and the long carry method on the right:
Traditional Carry Method Long Carry Method
vs.
Template:Brown carry the 1 until it is one digit past the "string" below
1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 cross out the "string",
+ 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 + 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 and cross out the digit that was added to it
——————————————————————— ——————————————————————
= 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1
The top row shows the carry bits used. Instead of the standard carry from one column to the next, the lowest-ordered "1" with a "1" in the corresponding place value beneath it may be added and a "1" may be carried to one digit past the end of the series. The "used" numbers must be crossed off, since they are already added. Other long strings may likewise be cancelled using the same technique. Then, simply add together any remaining digits normally. Proceeding in this manner gives the final answer of 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 12 (164910). In our simple example using small numbers, the traditional carry method required eight carry operations, yet the long carry method required only two, representing a substantial reduction of effort.
Addition table
| 0 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 10 |
The binary addition table is similar, but not the same, as the truth table of the logical disjunction operation . The difference is that , while .
Subtraction
Subtraction works in much the same way:
- 0 − 0 → 0
- 0 − 1 → 1, borrow 1
- 1 − 0 → 1
- 1 − 1 → 0
Subtracting a "1" digit from a "0" digit produces the digit "1", while 1 will have to be subtracted from the next column. This is known as borrowing. The principle is the same as for carrying. When the result of a subtraction is less than 0, the least possible value of a digit, the procedure is to "borrow" the deficit divided by the radix (that is, 10/10) from the left, subtracting it from the next positional value.
* * * * (starred columns are borrowed from) 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 − 1 0 1 1 1 ---------------- = 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
* (starred columns are borrowed from) 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 - 1 0 1 0 1 1 ---------------- = 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
Subtracting a positive number is equivalent to adding a negative number of equal absolute value. Computers use signed number representations to handle negative numbers—most commonly the two's complement notation. Such representations eliminate the need for a separate "subtract" operation. Using two's complement notation subtraction can be summarized by the following formula:
- A − B = A + not B + 1
Multiplication
Multiplication in binary is similar to its decimal counterpart. Two numbers Template:Varserif and Template:Varserif can be multiplied by partial products: for each digit in Template:Varserif, the product of that digit in Template:Varserif is calculated and written on a new line, shifted leftward so that its rightmost digit lines up with the digit in Template:Varserif that was used. The sum of all these partial products gives the final result.
Since there are only two digits in binary, there are only two possible outcomes of each partial multiplication:
- If the digit in Template:Varserif is 0, the partial product is also 0
- If the digit in Template:Varserif is 1, the partial product is equal to Template:Varserif
For example, the binary numbers 1011 and 1010 are multiplied as follows:
1 0 1 1 (Template:Varserif) × 1 0 1 0 (Template:Varserif) --------- 0 0 0 0 ← Corresponds to the rightmost 'zero' in Template:Varserif + 1 0 1 1 ← Corresponds to the next 'one' in Template:Varserif + 0 0 0 0 + 1 0 1 1 --------------- = 1 1 0 1 1 1 0
Binary numbers can also be multiplied with bits after a binary point:
1 0 1 . 1 0 1 Template:Varserif (5.625 in decimal) × 1 1 0 . 0 1 Template:Varserif (6.25 in decimal) ------------------- 1 . 0 1 1 0 1 ← Corresponds to a 'one' in Template:Varserif + 0 0 . 0 0 0 0 ← Corresponds to a 'zero' in Template:Varserif + 0 0 0 . 0 0 0 + 1 0 1 1 . 0 1 + 1 0 1 1 0 . 1 --------------------------- = 1 0 0 0 1 1 . 0 0 1 0 1 (35.15625 in decimal)
See also Booth's multiplication algorithm.
Multiplication table
| 0 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
The binary multiplication table is the same as the truth table of the logical conjunction operation .
Division
Template:Main Template:See also
Long division in binary is again similar to its decimal counterpart.
In the example below, the divisor is 1012, or 5 in decimal, while the dividend is 110112, or 27 in decimal. The procedure is the same as that of decimal long division; here, the divisor 1012 goes into the first three digits 1102 of the dividend one time, so a "1" is written on the top line. This result is multiplied by the divisor, and subtracted from the first three digits of the dividend; the next digit (a "1") is included to obtain a new three-digit sequence:
1
___________
1 0 1 ) 1 1 0 1 1
− 1 0 1
-----
0 0 1
The procedure is then repeated with the new sequence, continuing until the digits in the dividend have been exhausted:
1 0 1
___________
1 0 1 ) 1 1 0 1 1
− 1 0 1
-----
1 1 1
− 1 0 1
-----
0 1 0
Thus, the quotient of 110112 divided by 1012 is 1012, as shown on the top line, while the remainder, shown on the bottom line, is 102. In decimal, this corresponds to the fact that 27 divided by 5 is 5, with a remainder of 2.
Aside from long division, one can also devise the procedure so as to allow for over-subtracting from the partial remainder at each iteration, thereby leading to alternative methods which are less systematic, but more flexible as a result.
Square root
The process of taking a binary square root digit by digit is the same as for a decimal square root and is explained here. An example is:
1 0 0 1
---------
√ 1010001
1
---------
101 01
0
--------
1001 100
0
--------
10001 10001
10001
-------
0
Bitwise operations
Template:Main Though not directly related to the numerical interpretation of binary symbols, sequences of bits may be manipulated using Boolean logical operators. When a string of binary symbols is manipulated in this way, it is called a bitwise operation; the logical operators AND, OR, and XOR may be performed on corresponding bits in two binary numerals provided as input. The logical NOT operation may be performed on individual bits in a single binary numeral provided as input. Sometimes, such operations may be used as arithmetic short-cuts, and may have other computational benefits as well. For example, an arithmetic shift left of a binary number is the equivalent of multiplication by a (positive, integral) power of 2.
Conversion to and from other numeral systems
Decimal to Binary
To convert from a base-10 integer to its base-2 (binary) equivalent, the number is divided by two. The remainder is the least-significant bit. The quotient is again divided by two; its remainder becomes the next least significant bit. This process repeats until a quotient of one is reached. The sequence of remainders (including the final quotient of one) forms the binary value, as each remainder must be either zero or one when dividing by two. For example, (357)10 is expressed as (101100101)2.[4]
Binary to Decimal
Conversion from base-2 to base-10 simply inverts the preceding algorithm. The bits of the binary number are used one by one, starting with the most significant (leftmost) bit. Beginning with the value 0, the prior value is doubled, and the next bit is then added to produce the next value. This can be organized in a multi-column table. For example, to convert 100101011012 to decimal:
| Prior value | × 2 + | Next bit | Next value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | × 2 + | 1 | = 1 |
| 1 | × 2 + | 0 | = 2 |
| 2 | × 2 + | 0 | = 4 |
| 4 | × 2 + | 1 | = 9 |
| 9 | × 2 + | 0 | = 18 |
| 18 | × 2 + | 1 | = 37 |
| 37 | × 2 + | 0 | = 74 |
| 74 | × 2 + | 1 | = 149 |
| 149 | × 2 + | 1 | = 299 |
| 299 | × 2 + | 0 | = 598 |
| 598 | × 2 + | 1 | = 1197 |
The result is 119710. The first Prior Value of 0 is simply an initial decimal value. This method is an application of the Horner scheme.
| Binary | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decimal | 1×210 + | 0×29 + | 0×28 + | 1×27 + | 0×26 + | 1×25 + | 0×24 + | 1×23 + | 1×22 + | 0×21 + | 1×20 = | 1197 |
The fractional parts of a number are converted with similar methods. They are again based on the equivalence of shifting with doubling or halving.
In a fractional binary number such as 0.110101101012, the first digit is , the second , etc. So if there is a 1 in the first place after the decimal, then the number is at least , and vice versa. Double that number is at least 1. This suggests the algorithm: Repeatedly double the number to be converted, record if the result is at least 1, and then throw away the integer part.
For example, 10, in binary, is:
| Converting | Result |
|---|---|
| 0. | |
| 0.0 | |
| 0.01 | |
| 0.010 | |
| 0.0101 |
Thus the repeating decimal fraction 0.Template:Overline... is equivalent to the repeating binary fraction 0.Template:Overline... .
Or for example, 0.110, in binary, is:
| Converting | Result |
|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0. |
| 0.1 × 2 = 0.2 < 1 | 0.0 |
| 0.2 × 2 = 0.4 < 1 | 0.00 |
| 0.4 × 2 = 0.8 < 1 | 0.000 |
| 0.8 × 2 = 1.6 ≥ 1 | 0.0001 |
| 0.6 × 2 = 1.2 ≥ 1 | 0.00011 |
| 0.2 × 2 = 0.4 < 1 | 0.000110 |
| 0.4 × 2 = 0.8 < 1 | 0.0001100 |
| 0.8 × 2 = 1.6 ≥ 1 | 0.00011001 |
| 0.6 × 2 = 1.2 ≥ 1 | 0.000110011 |
| 0.2 × 2 = 0.4 < 1 | 0.0001100110 |
This is also a repeating binary fraction 0.0Template:Overline... . It may come as a surprise that terminating decimal fractions can have repeating expansions in binary. It is for this reason that many are surprised to discover that 0.1 + ... + 0.1, (10 additions) differs from 1 in floating point arithmetic. In fact, the only binary fractions with terminating expansions are of the form of an integer divided by a power of 2, which 1/10 is not.
The final conversion is from binary to decimal fractions. The only difficulty arises with repeating fractions, but otherwise the method is to shift the fraction to an integer, convert it as above, and then divide by the appropriate power of two in the decimal base. For example:
Another way of converting from binary to decimal, often quicker for a person familiar with hexadecimal, is to do so indirectly—first converting (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} in binary) into (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} in hexadecimal) and then converting (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} in hexadecimal) into (Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} in decimal).
For very large numbers, these simple methods are inefficient because they perform a large number of multiplications or divisions where one operand is very large. A simple divide-and-conquer algorithm is more effective asymptotically: given a binary number, it is divided by 10k, where k is chosen so that the quotient roughly equals the remainder; then each of these pieces is converted to decimal and the two are concatenated. Given a decimal number, it can be split into two pieces of about the same size, each of which is converted to binary, whereupon the first converted piece is multiplied by 10k and added to the second converted piece, where k is the number of decimal digits in the second, least-significant piece before conversion.
Hexadecimal
Template:Main Template:Hexadecimal table Binary may be converted to and from hexadecimal more easily. This is because the radix of the hexadecimal system (16) is a power of the radix of the binary system (2). More specifically, 16 = 24, so it takes four digits of binary to represent one digit of hexadecimal, as shown in the adjacent table.
To convert a hexadecimal number into its binary equivalent, simply substitute the corresponding binary digits:
- 3A16 = 0011 10102
- E716 = 1110 01112
To convert a binary number into its hexadecimal equivalent, divide it into groups of four bits. If the number of bits isn't a multiple of four, simply insert extra 0 bits at the left (called padding). For example:
- 10100102 = 0101 0010 grouped with padding = 5216
- 110111012 = 1101 1101 grouped = DD16
To convert a hexadecimal number into its decimal equivalent, multiply the decimal equivalent of each hexadecimal digit by the corresponding power of 16 and add the resulting values:
- C0E716 = (12 × 163) + (0 × 162) + (14 × 161) + (7 × 160) = (12 × 4096) + (0 × 256) + (14 × 16) + (7 × 1) = 49,38310
Octal
Template:Main Binary is also easily converted to the octal numeral system, since octal uses a radix of 8, which is a power of two (namely, 23, so it takes exactly three binary digits to represent an octal digit). The correspondence between octal and binary numerals is the same as for the first eight digits of hexadecimal in the table above. Binary 000 is equivalent to the octal digit 0, binary 111 is equivalent to octal 7, and so forth.
| Octal | Binary |
|---|---|
| 0 | 000 |
| 1 | 001 |
| 2 | 010 |
| 3 | 011 |
| 4 | 100 |
| 5 | 101 |
| 6 | 110 |
| 7 | 111 |
Converting from octal to binary proceeds in the same fashion as it does for hexadecimal:
- 658 = 110 1012
- 178 = 001 1112
And from binary to octal:
- 1011002 = 101 1002 grouped = 548
- 100112 = 010 0112 grouped with padding = 238
And from octal to decimal:
- 658 = (6 × 81) + (5 × 80) = (6 × 8) + (5 × 1) = 5310
- 1278 = (1 × 82) + (2 × 81) + (7 × 80) = (1 × 64) + (2 × 8) + (7 × 1) = 8710
Representing real numbers
Non-integers can be represented by using negative powers, which are set off from the other digits by means of a radix point (called a decimal point in the decimal system). For example, the binary number 11.012 means:
| 1 × 21 | (1 × 2 = 2) | plus |
| 1 × 20 | (1 × 1 = 1) | plus |
| 0 × 2−1 | (0 × Template:Frac = 0) | plus |
| 1 × 2−2 | (1 × Template:Frac = 0.25) |
For a total of 3.25 decimal.
All dyadic rational numbers Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{p}{2^a}} have a terminating binary numeral—the binary representation has a finite number of terms after the radix point. Other rational numbers have binary representation, but instead of terminating, they recur, with a finite sequence of digits repeating indefinitely. For instance
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1_{10}}{3_{10}} = \frac{1_2}{11_2} = 0.01010101\overline{01}\ldots\,_2 }
- Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{12_{10}}{17_{10}} = \frac{1100_2}{10001_2} = 0.10110100 10110100\overline{10110100}\ldots\,_2 }
The phenomenon that the binary representation of any rational is either terminating or recurring also occurs in other radix-based numeral systems. See, for instance, the explanation in decimal. Another similarity is the existence of alternative representations for any terminating representation, relying on the fact that 0.111111... is the sum of the geometric series 2−1 + 2−2 + 2−3 + ... which is 1.
Binary numerals which neither terminate nor recur represent irrational numbers. For instance,
- 0.10100100010000100000100... does have a pattern, but it is not a fixed-length recurring pattern, so the number is irrational
- 1.0110101000001001111001100110011111110... is the binary representation of Failed to parse (MathML with SVG or PNG fallback (recommended for modern browsers and accessibility tools): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{2}} , the square root of 2, another irrational. It has no discernible pattern.
Licensing
Content obtained and/or adapted from:
- Radix, Wikipedia under a CC BY-SA license