|
|
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ==Inverse function==
| |
| | The function <math>g</math> is the inverse of the one-to-one function <math>f</math> if and only if the following are true:<br/> | | The function <math>g</math> is the inverse of the one-to-one function <math>f</math> if and only if the following are true:<br/> |
| | :<math>g(f(x))=x \,</math> | | :<math>g(f(x))=x \,</math> |
Revision as of 13:59, 5 October 2021
The function  is the inverse of the one-to-one function
is the inverse of the one-to-one function  if and only if the following are true:
if and only if the following are true:


The inverse of function  is denoted as
is denoted as  .
.
Geometrically  is the reflection of
is the reflection of  across the line
across the line  .
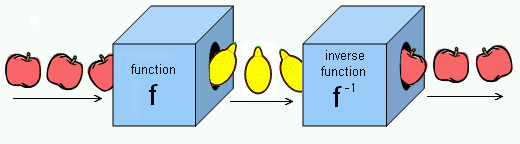
Conceptually, using the box analogy, a function's inverse box undoes what the function's
regular box does.
.
Conceptually, using the box analogy, a function's inverse box undoes what the function's
regular box does.
 Example:
Example:








To find the inverse of a function, remember that when we use  as an input to
as an input to  the result is
the result is  . So start by writing
. So start by writing  and solve for
and solve for 
Example:
Suppose: Then
Then 



The Domain of an inverse function is exactly the same as the Range of the original function. If the Range of the original function is limited in some way, the inverse of a function will require a restricted domain.
Example:





 The Range of
The Range of  is
is  . So the Domain of
. So the Domain of  is
is  .
.
One-to-one function
A function that for every input there exists an output unique to that input.
Equivalently, we may say that a function  is called one-to-one if for all
is called one-to-one if for all
 implies that
implies that  where A is the domain set of f and
both x and x' are members of that set.
where A is the domain set of f and
both x and x' are members of that set.
Horizontal Line Test
If no horizontal line intersects the graph of a function in more than one place then the function is a one-to-one function.
Resources






























